Several Makefiles are used in the projects documented on this website to automate building, flashing, and cleaning embedded projects. This article explores how Makefiles work across different development environments and provides practical examples for AVR and STM32 microcontrollers.
Makefile for AVR Projects
For educational purposes and to understand AVR microcontroller development in a pure GNU/Linux environment, I created a comprehensive Makefile for the AVR RGB LED Control project.
Also, I wrote an article to explain how to use them with VSCode and Linux tools: Build and flash AVR projects in Linux
Basic AVR Makefile Structure
To create this Makefile, I used the Microchip Studio autogenerated Makefile as a model and adapted it to my small project.
# Makefile for building and flashing ATMEGA328p
# Variables
MCU = atmega328p
F_CPU = 8000000
SRC = src
BUILD_DIR = bin
BINARY_NAME = RGB_control
PROGRAMMER = usbasp
PORT = usb
LFUSE = 0xD2
HFUSE =
EFUSE =
# Compiler and linker flags
CFLAGS=-mmcu=$(MCU) -Wall -Os -DF_CPU=$(F_CPU)
LDFLAGS= -p $(MCU) -c $(PROGRAMMER) -P $(PORT)
# Rules
all: $(BUILD_DIR)/$(BINARY_NAME).hex
$(BUILD_DIR)/$(BINARY_NAME).elf: $(SRC)
@mkdir -p $(BUILD_DIR)
avr-gcc $(CFLAGS) $(SRC)/*.c $(SRC)/LED_control/*.c $(SRC)/timer_control/*.c -o $(BUILD_DIR)/$(BINARY_NAME).elf
$(BUILD_DIR)/$(BINARY_NAME).hex: $(BUILD_DIR)/$(BINARY_NAME).elf
avr-objcopy -j .text -j .data -O ihex $(BUILD_DIR)/$(BINARY_NAME).elf $(BUILD_DIR)/$(BINARY_NAME).hex -v
flash: $(BUILD_DIR)/$(BINARY_NAME).hex
avrdude $(LDFLAGS) -U flash:w:$(BUILD_DIR)/$(BINARY_NAME).hex:i
readFuses:
avrdude $(LDFLAGS) -U efuse:r:-:h -U hfuse:r:-:h -U lfuse:r:-:h
writeLowFuse:
avrdude $(LDFLAGS) -U lfuse:w:0xD2:m
clean:
rm -rf $(BUILD_DIR)
.PHONY: all flash clean
While researching to write this article, I gained a better understanding of how Makefiles work, and with the help of an AI chatbot, I was able to improve this Makefile.
# ==============================================================================
# AVR Makefile for ATMEGA328p - RGB_control Example
# ==============================================================================
# Hardware Configuration
MCU = atmega328p
F_CPU = 8000000UL
PROGRAMMER = usbasp
PORT = usb
# Fuse Settings (8MHz internal oscillator)
LFUSE = 0xD2
HFUSE = 0xD9
EFUSE = 0xFF
# Project Structure
PROJECT_NAME = RGB_control
SRC_DIR = src
BUILD_DIR = bin
INCLUDE_DIR = include
# Source Files Discovery
SOURCES = $(wildcard $(SRC_DIR)/*.c) \
$(wildcard $(SRC_DIR)/*/*.c) #\ $(wildcard $(SRC_DIR)/*/*/*.c)
# Object Files (convert .c to .o and place in build directory)
OBJECTS = $(SOURCES:$(SRC_DIR)/%.c=$(BUILD_DIR)/%.o)
# Dependency Files (for automatic header dependency tracking)
DEPS = $(OBJECTS:.o=.d)
# Compiler and Tools
CC = avr-gcc
OBJCOPY = avr-objcopy
OBJDUMP = avr-objdump
SIZE = avr-size
AVRDUDE = avrdude
# Compiler Flags
CFLAGS = -mmcu=$(MCU) \
-DF_CPU=$(F_CPU) \
-I$(INCLUDE_DIR) \
-Os \
-Wall \
-Wundef \
-ffunction-sections \
-fdata-sections \
-MMD -MP
# Linker Flags
LDFLAGS = -mmcu=$(MCU) \
-Wl,--gc-sections \
-Wl,-Map=$(BUILD_DIR)/$(PROJECT_NAME).map
# AVRdude Flags
AVRDUDE_FLAGS = -p $(MCU) \
-c $(PROGRAMMER) \
-P $(PORT) \
# ==============================================================================
# Build Rules
# ==============================================================================
# Default target
all: $(BUILD_DIR)/$(PROJECT_NAME).hex size
# Create object files from C source files
$(BUILD_DIR)/%.o: $(SRC_DIR)/%.c
@echo "Compiling: $<"
@mkdir -p $(dir $@)
@$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -c $< -o $@
# Link object files to create ELF executable
$(BUILD_DIR)/$(PROJECT_NAME).elf: $(OBJECTS)
@echo "Linking: $@"
@mkdir -p $(BUILD_DIR)
@$(CC) $(LDFLAGS) $(OBJECTS) -o $@
# Convert ELF to Intel HEX format
$(BUILD_DIR)/$(PROJECT_NAME).hex: $(BUILD_DIR)/$(PROJECT_NAME).elf
@echo "Creating HEX file: $@"
@$(OBJCOPY) -j .text -j .data -O ihex $< $@
# Display memory usage information
size: $(BUILD_DIR)/$(PROJECT_NAME).elf
@echo ""
@echo "Memory Usage:"
@$(SIZE) --format=avr --mcu=$(MCU) $<
@echo ""
# Create assembly listing (useful for debugging)
$(BUILD_DIR)/$(PROJECT_NAME).lss: $(BUILD_DIR)/$(PROJECT_NAME).elf
@echo "Creating assembly listing: $@"
@$(OBJDUMP) -h -S $< > $@
# ==============================================================================
# Programming Rules
# ==============================================================================
# Flash the program to microcontroller
flash: $(BUILD_DIR)/$(PROJECT_NAME).hex
@echo "Flashing $(PROJECT_NAME).hex to $(MCU)..."
@$(AVRDUDE) $(AVRDUDE_FLAGS) -U flash:w:$<:i -v
# Verify the flashed program
verify: $(BUILD_DIR)/$(PROJECT_NAME).hex
@echo "Verifying flash memory..."
@$(AVRDUDE) $(AVRDUDE_FLAGS) -U flash:v:$<:i
# ==============================================================================
# Fuse Programming Rules
# ==============================================================================
# Read current fuse settings
rfuses:
@echo "Reading current fuse settings..."
@$(AVRDUDE) $(AVRDUDE_FLAGS) \
-U lfuse:r:-:h \
-U hfuse:r:-:h \
-U efuse:r:-:h
# Write all fuses (DANGEROUS - can brick your MCU!)
wfuses:
@echo "WARNING: Writing fuses can brick your microcontroller!"
@echo "Current settings: LFUSE=$(LFUSE), HFUSE=$(HFUSE), EFUSE=$(EFUSE)"
@read -p "Are you sure you want to continue? (yes/no): " confirm && \
if [ "$$confirm" = "yes" ]; then \
$(AVRDUDE) $(AVRDUDE_FLAGS) \
-U lfuse:w:$(LFUSE):m \
-U hfuse:w:$(HFUSE):m \
-U efuse:w:$(EFUSE):m; \
else \
echo "Fuse programming cancelled."; \
fi
# Write only low fuse (safer for clock settings)
wlfuse:
@echo "Writing low fuse: $(LFUSE)"
@$(AVRDUDE) $(AVRDUDE_FLAGS) -U lfuse:w:$(LFUSE):m
# ==============================================================================
# Utility Rules
# ==============================================================================
# Clean build artifacts
clean:
@echo "Cleaning build directory..."
@rm -rf $(BUILD_DIR)
# Show project information
info:
@echo "Project Information:"
@echo " Project Name: $(PROJECT_NAME)"
@echo " MCU: $(MCU)"
@echo " F_CPU: $(F_CPU) Hz"
@echo " Programmer: $(PROGRAMMER)"
@echo " Port: $(PORT)"
@echo ""
@echo "Fuse Settings:"
@echo " Low Fuse: $(LFUSE)"
@echo " High Fuse: $(HFUSE)"
@echo " Extended Fuse:$(EFUSE)"
@echo ""
@echo "Source Files:"
@$(foreach src,$(SOURCES),echo " $(src)";)
# Display available targets
help:
@echo "Available Make targets:"
@echo ""
@echo "Build targets:"
@echo " all - Build the complete project (default)"
@echo " clean - Remove build directory"
@echo " distclean - Deep clean (removes all build artifacts)"
@echo " size - Display memory usage information"
@echo ""
@echo "Programming targets:"
@echo " flash - Program the microcontroller"
@echo " verify - Verify the programmed flash"
@echo ""
@echo "Fuse targets:"
@echo " rfuses - Read current fuse settings"
@echo " wfuses - Write all fuses (DANGEROUS!)"
@echo " wlfuse - Write only low fuse"
@echo ""
@echo "Utility targets:"
@echo " info - Show project information"
@echo " help - Show this help message"
# ==============================================================================
# Special Targets
# ==============================================================================
# Prevent Make from deleting intermediate files
.PRECIOUS: $(BUILD_DIR)/%.o $(BUILD_DIR)/%.elf
# Declare phony targets (targets that don't create files)
.PHONY: all clean flash verify rfuses wfuses wlfuse info help size
# Include dependency files (for automatic recompilation when headers change)
-include $(DEPS)
Key Features of This Makefile
-
Automatic Source Discovery: Uses
wildcardto find all.cfiles in the source directory. -
Dependency Tracking: Automatically tracks header dependencies using
-MMD -MPflags. -
Memory Optimization: Uses
-Osfor size optimization and--gc-sectionsfor dead code elimination. - Safety Features: Includes confirmation prompts for potentially dangerous operations like fuse programming.
- User-Friendly Output: Provides clear status messages and help information.
Working with IDEs
Most IDEs have tools to generate Makefiles automatically. Throughout my experience, I have used Eclipse-based IDEs to build projects in C and C++. Years ago, I had no idea that the Makefile was created by the IDE tools until I needed to modify the Makefiles myself. Like most of my learning, it was a process of trying, modifying, failing, correcting, and trying again.
Eclipse
When using Eclipse-based IDEs like STM32CubeIDE, the Makefile is modified through the project properties. With a project open, you can access the properties as follows:
- Access Project Properties: Go to the Project menu and click on Properties.
-
Configure Build Settings: Check C/C++ Build → Settings → Tool Settings:
- MCU/MPU Toolchain: Configure the ARM toolchain (IDE option or external)
- MCU/MPU Settings: View CPU information
-
MCU/MPU Post build outputs: Set output formats for binaries
- MCU/MPU GCC Assembler: Configure preprocessor and assembler options
-
MCU/MPU GCC Compiler: Manage compiler options
- MCU/MPU GCC Linker: Configure linking options
- Understanding Generated Makefiles: The IDE stores the makefile in the Release/Debug path. Here’s an example of what gets generated:
-include ../makefile.init
RM := rm -rf
# All of the sources participating in the build are defined here
-include sources.mk
-include Drivers/STM32F1xx_HAL_Driver/Src/subdir.mk
-include Core/Startup/subdir.mk
-include Core/Src/subdir.mk
-include objects.mk
ifneq ($(MAKECMDGOALS),clean)
ifneq ($(strip $(S_DEPS)),)
-include $(S_DEPS)
endif
ifneq ($(strip $(S_UPPER_DEPS)),)
-include $(S_UPPER_DEPS)
endif
ifneq ($(strip $(C_DEPS)),)
-include $(C_DEPS)
endif
endif
-include ../makefile.defs
OPTIONAL_TOOL_DEPS := \
$(wildcard ../makefile.defs) \
$(wildcard ../makefile.init) \
$(wildcard ../makefile.targets) \
BUILD_ARTIFACT_NAME := testOfSTM32F103
BUILD_ARTIFACT_EXTENSION := elf
BUILD_ARTIFACT_PREFIX :=
BUILD_ARTIFACT := $(BUILD_ARTIFACT_PREFIX)$(BUILD_ARTIFACT_NAME)$(if $(BUILD_ARTIFACT_EXTENSION),.$(BUILD_ARTIFACT_EXTENSION),)
# Add inputs and outputs from these tool invocations to the build variables
EXECUTABLES += \
testOfSTM32F103.elf \
MAP_FILES += \
testOfSTM32F103.map \
SIZE_OUTPUT += \
default.size.stdout \
OBJDUMP_LIST += \
testOfSTM32F103.list \
# All Target
all: main-build
# Main-build Target
main-build: testOfSTM32F103.elf secondary-outputs
# Tool invocations
testOfSTM32F103.elf testOfSTM32F103.map: $(OBJS) $(USER_OBJS) /home/octavioguendulain/STM32CubeIDE/workspace_1.16.1/testOfSTM32F103/STM32F103C8TX_FLASH.ld makefile objects.list $(OPTIONAL_TOOL_DEPS)
arm-none-eabi-gcc -o "testOfSTM32F103.elf" @"objects.list" $(USER_OBJS) $(LIBS) -mcpu=cortex-m3 -T"/home/octavioguendulain/STM32CubeIDE/workspace_1.16.1/testOfSTM32F103/STM32F103C8TX_FLASH.ld" --specs=nosys.specs -Wl,-Map="testOfSTM32F103.map" -Wl,--gc-sections -static --specs=nano.specs -mfloat-abi=soft -mthumb -Wl,--start-group -lc -lm -Wl,--end-group
@echo 'Finished building target: $@'
@echo ' '
default.size.stdout: $(EXECUTABLES) makefile objects.list $(OPTIONAL_TOOL_DEPS)
arm-none-eabi-size $(EXECUTABLES)
@echo 'Finished building: $@'
@echo ' '
testOfSTM32F103.list: $(EXECUTABLES) makefile objects.list $(OPTIONAL_TOOL_DEPS)
arm-none-eabi-objdump -h -S $(EXECUTABLES) > "testOfSTM32F103.list"
@echo 'Finished building: $@'
@echo ' '
# Other Targets
clean:
-$(RM) default.size.stdout testOfSTM32F103.elf testOfSTM32F103.list testOfSTM32F103.map
-@echo ' '
secondary-outputs: $(SIZE_OUTPUT) $(OBJDUMP_LIST)
fail-specified-linker-script-missing:
@echo 'Error: Cannot find the specified linker script. Check the linker settings in the build configuration.'
@exit 2
warn-no-linker-script-specified:
@echo 'Warning: No linker script specified. Check the linker settings in the build configuration.'
.PHONY: all clean dependents main-build fail-specified-linker-script-missing warn-no-linker-script-specified
-include ../makefile.targets
Key Learning Point: When you modify IDE settings, the changes are reflected in the generated Makefiles.
If you change the settings you can see the changes in makefile. As an example:
- Active the binary file and s-record as outputs in Post build output.
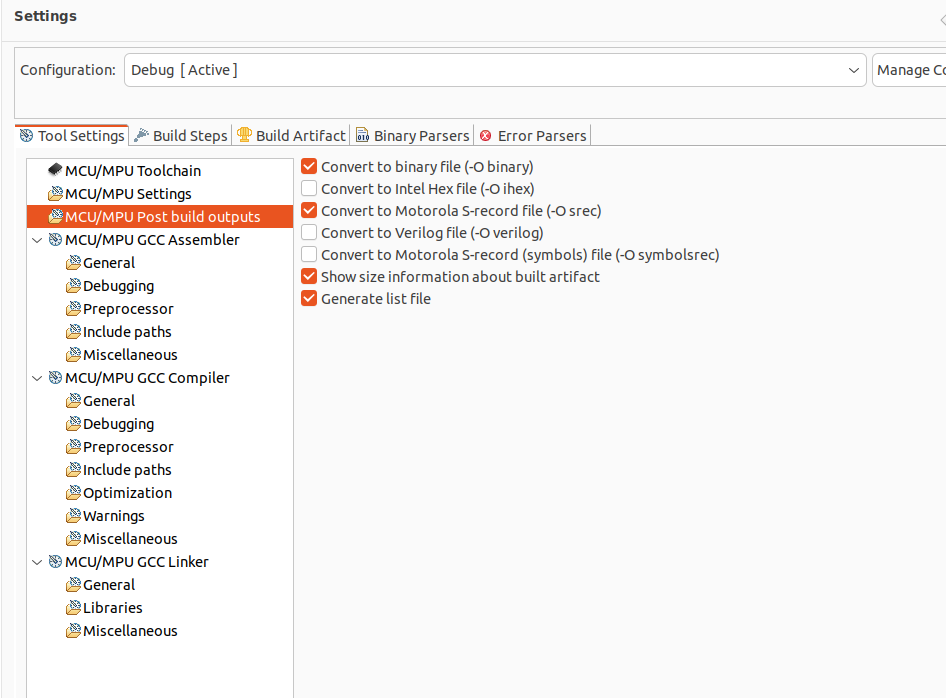
-include ../makefile.init
RM := rm -rf
# All of the sources participating in the build are defined here
-include sources.mk
-include Drivers/STM32F1xx_HAL_Driver/Src/subdir.mk
-include Core/Startup/subdir.mk
-include Core/Src/subdir.mk
-include objects.mk
ifneq ($(MAKECMDGOALS),clean)
ifneq ($(strip $(S_DEPS)),)
-include $(S_DEPS)
endif
ifneq ($(strip $(S_UPPER_DEPS)),)
-include $(S_UPPER_DEPS)
endif
ifneq ($(strip $(C_DEPS)),)
-include $(C_DEPS)
endif
endif
-include ../makefile.defs
OPTIONAL_TOOL_DEPS := \
$(wildcard ../makefile.defs) \
$(wildcard ../makefile.init) \
$(wildcard ../makefile.targets) \
BUILD_ARTIFACT_NAME := testOfSTM32F103
BUILD_ARTIFACT_EXTENSION := elf
BUILD_ARTIFACT_PREFIX :=
BUILD_ARTIFACT := $(BUILD_ARTIFACT_PREFIX)$(BUILD_ARTIFACT_NAME)$(if $(BUILD_ARTIFACT_EXTENSION),.$(BUILD_ARTIFACT_EXTENSION),)
# Add inputs and outputs from these tool invocations to the build variables
EXECUTABLES += \
testOfSTM32F103.elf \
MAP_FILES += \
testOfSTM32F103.map \
SIZE_OUTPUT += \
default.size.stdout \
OBJDUMP_LIST += \
testOfSTM32F103.list \
OBJCOPY_BIN += \
testOfSTM32F103.bin \
OBJCOPY_SREC += \
testOfSTM32F103.srec \
# All Target
all: main-build
# Main-build Target
main-build: testOfSTM32F103.elf secondary-outputs
# Tool invocations
testOfSTM32F103.elf testOfSTM32F103.map: $(OBJS) $(USER_OBJS) /home/octavioguendulain/STM32CubeIDE/workspace_1.16.1/testOfSTM32F103/STM32F103C8TX_FLASH.ld makefile objects.list $(OPTIONAL_TOOL_DEPS)
arm-none-eabi-gcc -o "testOfSTM32F103.elf" @"objects.list" $(USER_OBJS) $(LIBS) -mcpu=cortex-m3 -T"/home/octavioguendulain/STM32CubeIDE/workspace_1.16.1/testOfSTM32F103/STM32F103C8TX_FLASH.ld" --specs=nosys.specs -Wl,-Map="testOfSTM32F103.map" -Wl,--gc-sections -static --specs=nano.specs -mfloat-abi=soft -mthumb -Wl,--start-group -lc -lm -Wl,--end-group
@echo 'Finished building target: $@'
@echo ' '
default.size.stdout: $(EXECUTABLES) makefile objects.list $(OPTIONAL_TOOL_DEPS)
arm-none-eabi-size $(EXECUTABLES)
@echo 'Finished building: $@'
@echo ' '
testOfSTM32F103.list: $(EXECUTABLES) makefile objects.list $(OPTIONAL_TOOL_DEPS)
arm-none-eabi-objdump -h -S $(EXECUTABLES) > "testOfSTM32F103.list"
@echo 'Finished building: $@'
@echo ' '
testOfSTM32F103.bin: $(EXECUTABLES) makefile objects.list $(OPTIONAL_TOOL_DEPS)
arm-none-eabi-objcopy -O binary $(EXECUTABLES) "testOfSTM32F103.bin"
@echo 'Finished building: $@'
@echo ' '
testOfSTM32F103.srec: $(EXECUTABLES) makefile objects.list $(OPTIONAL_TOOL_DEPS)
arm-none-eabi-objcopy -O srec $(EXECUTABLES) "testOfSTM32F103.srec"
@echo 'Finished building: $@'
@echo ' '
# Other Targets
clean:
-$(RM) default.size.stdout testOfSTM32F103.bin testOfSTM32F103.elf testOfSTM32F103.list testOfSTM32F103.map testOfSTM32F103.srec
-@echo ' '
secondary-outputs: $(SIZE_OUTPUT) $(OBJDUMP_LIST) $(OBJCOPY_BIN) $(OBJCOPY_SREC)
fail-specified-linker-script-missing:
@echo 'Error: Cannot find the specified linker script. Check the linker settings in the build configuration.'
@exit 2
warn-no-linker-script-specified:
@echo 'Warning: No linker script specified. Check the linker settings in the build configuration.'
.PHONY: all clean dependents main-build fail-specified-linker-script-missing warn-no-linker-script-specified
-include ../makefile.targets
-
Configure Optimize for size (-Os) in GCC Compiler/Optimization (In the case of Debug)
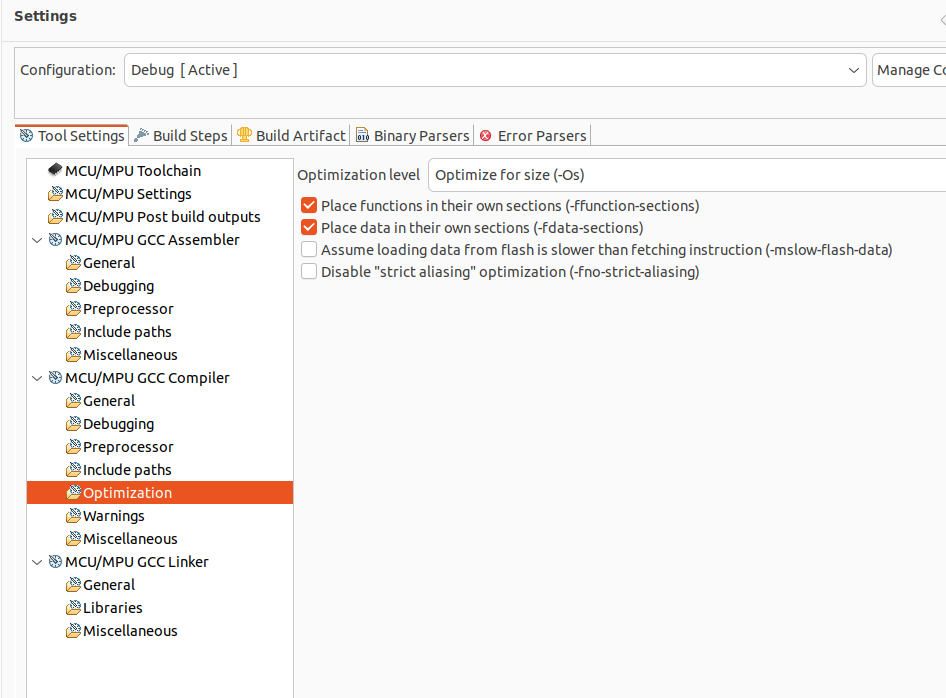
The changes are stored in the subdir.mk files
diff --git a/Debug/Core/Src/subdir.mk b/Debug/Core/Src/subdir.mk
index 878ade1..74e68c0 100644
--- a/Debug/Core/Src/subdir.mk
+++ b/Debug/Core/Src/subdir.mk
@@ -31,7 +31,7 @@ C_DEPS += \
# Each subdirectory must supply rules for building sources it contributes
Core/Src/%.o Core/Src/%.su Core/Src/%.cyclo: ../Core/Src/%.c Core/Src/subdir.mk
- arm-none-eabi-gcc "$<" -mcpu=cortex-m3 -std=gnu11 -g3 -DDEBUG -DUSE_HAL_DRIVER -DSTM32F103xB -c -I../Core/Inc -I../Drivers/STM32F1xx_HAL_Driver/Inc/Legacy -I../Drivers/STM32F1xx_HAL_Driver/Inc -I../Drivers/CMSIS/Device/ST/STM32F1xx/Include -I../Drivers/CMSIS/Include -O0 -ffunction-sections -fdata-sections -Wall -fstack-usage -fcyclomatic-complexity -MMD -MP -MF"$(@:%.o=%.d)" -MT"$@" --specs=nano.specs -mfloat-abi=soft -mthumb -o "$@"
+ arm-none-eabi-gcc "$<" -mcpu=cortex-m3 -std=gnu11 -g3 -DDEBUG -DUSE_HAL_DRIVER -DSTM32F103xB -c -I../Core/Inc -I../Drivers/STM32F1xx_HAL_Driver/Inc/Legacy -I../Drivers/STM32F1xx_HAL_Driver/Inc -I../Drivers/CMSIS/Device/ST/STM32F1xx/Include -I../Drivers/CMSIS/Include -Os -ffunction-sections -fdata-sections -Wall -fstack-usage -fcyclomatic-complexity -MMD -MP -MF"$(@:%.o=%.d)" -MT"$@" --specs=nano.specs -mfloat-abi=soft -mthumb -o "$@"
clean: clean-Core-2f-Src
diff --git a/Debug/Drivers/STM32F1xx_HAL_Driver/Src/subdir.mk b/Debug/Drivers/STM32F1xx_HAL_Driver/Src/subdir.mk
index 372c133..629c746 100644
--- a/Debug/Drivers/STM32F1xx_HAL_Driver/Src/subdir.mk
+++ b/Debug/Drivers/STM32F1xx_HAL_Driver/Src/subdir.mk
@@ -58,7 +58,7 @@ C_DEPS += \
# Each subdirectory must supply rules for building sources it contributes
Drivers/STM32F1xx_HAL_Driver/Src/%.o Drivers/STM32F1xx_HAL_Driver/Src/%.su Drivers/STM32F1xx_HAL_Driver/Src/%.cyclo: ../Drivers/STM32F1xx_HAL_Driver/Src/%.c Drivers/STM32F1xx_HAL_Driver/Src/subdir.mk
- arm-none-eabi-gcc "$<" -mcpu=cortex-m3 -std=gnu11 -g3 -DDEBUG -DUSE_HAL_DRIVER -DSTM32F103xB -c -I../Core/Inc -I../Drivers/STM32F1xx_HAL_Driver/Inc/Legacy -I../Drivers/STM32F1xx_HAL_Driver/Inc -I../Drivers/CMSIS/Device/ST/STM32F1xx/Include -I../Drivers/CMSIS/Include -O0 -ffunction-sections -fdata-sections -Wall -fstack-usage -fcyclomatic-complexity -MMD -MP -MF"$(@:%.o=%.d)" -MT"$@" --specs=nano.specs -mfloat-abi=soft -mthumb -o "$@"
+ arm-none-eabi-gcc "$<" -mcpu=cortex-m3 -std=gnu11 -g3 -DDEBUG -DUSE_HAL_DRIVER -DSTM32F103xB -c -I../Core/Inc -I../Drivers/STM32F1xx_HAL_Driver/Inc/Legacy -I../Drivers/STM32F1xx_HAL_Driver/Inc -I../Drivers/CMSIS/Device/ST/STM32F1xx/Include -I../Drivers/CMSIS/Include -Os -ffunction-sections -fdata-sections -Wall -fstack-usage -fcyclomatic-complexity -MMD -MP -MF"$(@:%.o=%.d)" -MT"$@" --specs=nano.specs -mfloat-abi=soft -mthumb -o "$@"
clean: clean-Drivers-2f-STM32F1xx_HAL_Driver-2f-Src
Note:
My method for learning new tools is to examine multiple examples and understand what happens when building projects or executables. That’s why I show you how the autogenerated files change.
Makefile used for STM32 with GCC
For the projects documented on this website, the Makefiles were based on the structure provided by the OpenBLT bootloader. This served as a starting point to create customized Makefiles tailored to each project’s specific requirements.
SHELL = sh
#|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
#| Configure project name |
#|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
PROJ_NAME=openblt_stm32f103
#|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
#| Configure tool path |
#|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
# Configure the path to where the arm-none-eabi-gcc program is located. If the program
# is available on the path, then the TOOL_PATH variable can be left empty.
TOOL_PATH=/opt/arm-gnu-toolchain-14.2.rel1-x86_64-arm-none-eabi/bin/
#|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
#| Collect project files |
#|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
# Recursive wildcard function implementation. Example usages:
# $(call rwildcard, , *.c *.h)
# --> Returns all *.c and *.h files in the current directory and below
# $(call rwildcard, /lib/, *.c)
# --> Returns all *.c files in the /lib directory and below
rwildcard = $(strip $(foreach d,$(wildcard $1*),$(call rwildcard,$d/,$2) $(filter $(subst *,%,$2),$d)))
# Collect all application files in the current directory and its subdirectories, but
# exclude flash-layout.c as this one is directly included in a source file, when used.
PROJ_FILES = $(filter-out flash_layout.c, $(call rwildcard, , *.c *.h *.s))
# Collect bootloader core files
PROJ_FILES += $(wildcard ../Source-openBLT/*.c)
PROJ_FILES += $(wildcard ../Source-openBLT/*.h)
# Collect bootloader port files
PROJ_FILES += $(wildcard ../Source-openBLT/ARMCM3_STM32F1/*.c)
PROJ_FILES += $(wildcard ../Source-openBLT/ARMCM3_STM32F1/*.h)
# Collect bootloader port compiler specific files
PROJ_FILES += $(wildcard ../Source-openBLT/ARMCM3_STM32F1/GCC/*.c)
PROJ_FILES += $(wildcard ../Source-openBLT/ARMCM3_STM32F1/GCC/*.h)
#|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
#| Toolchain binaries |
#|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
RM = rm
CC = $(TOOL_PATH)arm-none-eabi-gcc
LN = $(TOOL_PATH)arm-none-eabi-gcc
OC = $(TOOL_PATH)arm-none-eabi-objcopy
OD = $(TOOL_PATH)arm-none-eabi-objdump
AS = $(TOOL_PATH)arm-none-eabi-gcc
SZ = $(TOOL_PATH)arm-none-eabi-size
#|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
#| Filter project files
#|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
PROJ_ASRCS = $(filter %.s,$(foreach file,$(PROJ_FILES),$(notdir $(file))))
PROJ_CSRCS = $(filter %.c,$(foreach file,$(PROJ_FILES),$(notdir $(file))))
#|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
#| Set important path variables |
#|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
VPATH = $(foreach path,$(sort $(foreach file,$(PROJ_FILES),$(dir $(file)))) $(subst \,/,$(OBJ_PATH)),$(path) :)
OBJ_PATH = obj
BIN_PATH = bin
INC_PATH = $(patsubst %/,%,$(patsubst %,-I%,$(sort $(foreach file,$(filter %.h,$(PROJ_FILES)),$(dir $(file))))))
LIB_PATH =
#|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
#| Options for toolchain binaries |
#|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
STDFLAGS = -mcpu=cortex-m3 -mthumb -std=gnu11 -fstack-usage -Wall -specs=nano.specs
STDFLAGS += -fdata-sections -ffunction-sections -Wall -g -Wno-strict-aliasing
OPTFLAGS = -Os -flto
DEPFLAGS = -MT $@ -MMD -MP -MF $(OBJ_PATH)/$*.d
CFLAGS = $(STDFLAGS) $(OPTFLAGS)
CFLAGS += -DUSE_FULL_LL_DRIVER -DUSE_HAL_DRIVER -DSTM32F103xB
CFLAGS += -D__weak="__attribute__((weak))" -D__packed="__attribute__((__packed__))"
CFLAGS += $(INC_PATH)
AFLAGS = $(CFLAGS)
LFLAGS = $(STDFLAGS) $(OPTFLAGS)
LFLAGS += -T"STM32F103C8TX_FLASH.ld" -Wl,-Map=$(BIN_PATH)/$(PROJ_NAME).map
LFLAGS += -Wl,--gc-sections $(LIB_PATH)
OFLAGS = -O srec
ODFLAGS = -x
SZFLAGS = -B -d
RMFLAGS = -f
#|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
#| Specify library files |
#|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
LIBS =
#|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
#| Define targets |
#|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
AOBJS = $(patsubst %.s,%.o,$(PROJ_ASRCS))
COBJS = $(patsubst %.c,%.o,$(PROJ_CSRCS))
#|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
#| Make ALL |
#|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
.PHONY: prepare_dirs
prepare_dirs:
mkdir -p $(OBJ_PATH)
mkdir -p $(BIN_PATH)
.PHONY: all
all: prepare_dirs $(BIN_PATH)/$(PROJ_NAME).srec $(BIN_PATH)/$(PROJ_NAME).bin
$(BIN_PATH)/$(PROJ_NAME).srec : $(BIN_PATH)/$(PROJ_NAME).elf
@$(OC) $< $(OFLAGS) $@
@$(OD) $(ODFLAGS) $< > $(BIN_PATH)/$(PROJ_NAME).map
@echo +++ Summary of memory consumption:
@$(SZ) $(SZFLAGS) $<
@echo +++ Build complete [$(notdir $@)]
$(BIN_PATH)/$(PROJ_NAME).elf : $(AOBJS) $(COBJS)
@echo +++ Linking [$(notdir $@)]
@$(LN) $(LFLAGS) -o $@ $(patsubst %.o,$(OBJ_PATH)/%.o,$(^F)) $(LIBS)
.PHONY: $(BIN_PATH)/$(PROJ_NAME).bin
$(BIN_PATH)/$(PROJ_NAME).bin:
@$(OC) -O binary $(BIN_PATH)/$(PROJ_NAME).elf $@
#|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
#| Compile and assemble |
#|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
$(AOBJS): %.o: %.s
@echo +++ Assembling [$(notdir $<)]
@$(AS) $(AFLAGS) -c $< -o $(OBJ_PATH)/$(@F)
$(COBJS): %.o: %.c $(OBJ_PATH)/%.d
@echo +++ Compiling [$(notdir $<)]
@$(CC) $(DEPFLAGS) $(CFLAGS) -c $< -o $(OBJ_PATH)/$(@F)
#|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
#| Make CLEAN |
#|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
.PHONY: clean
clean:
@echo +++ Cleaning build environment
@$(RM) $(RMFLAGS) $(foreach file,$(AOBJS),$(OBJ_PATH)/$(file))
@$(RM) $(RMFLAGS) $(foreach file,$(COBJS),$(OBJ_PATH)/$(file))
@$(RM) $(RMFLAGS) $(patsubst %.o,%.lst,$(foreach file,$(AOBJS),$(OBJ_PATH)/$(file)))
@$(RM) $(RMFLAGS) $(patsubst %.o,%.lst,$(foreach file,$(COBJS),$(OBJ_PATH)/$(file)))
@$(RM) $(RMFLAGS) $(patsubst %.o,%.d,$(foreach file,$(COBJS),$(OBJ_PATH)/$(file)))
@$(RM) $(RMFLAGS) $(patsubst %.o,%.su,$(foreach file,$(COBJS),$(OBJ_PATH)/$(file)))
@$(RM) $(RMFLAGS) $(BIN_PATH)/$(PROJ_NAME).elf $(BIN_PATH)/$(PROJ_NAME).*.su $(BIN_PATH)/$(PROJ_NAME).bin $(BIN_PATH)/$(PROJ_NAME).map
@$(RM) $(RMFLAGS) $(BIN_PATH)/$(PROJ_NAME).srec
@echo +++ Clean complete
#|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
#| Dependency generation |
#|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
DEPFILES := $(PROJ_CSRCS:%.c=$(OBJ_PATH)/%.d)
$(DEPFILES):
include $(wildcard $(DEPFILES))
Best Practices and Key Concepts
1. Variable Organization
- Configuration Variables: Place all configurable items (MCU, frequencies, paths) at the top.
- Tool Variables: Define all tools in one section for easy maintenance.
- Path Variables: Use consistent naming for directories (SRC_DIR, BUILD_DIR, etc.).
2. Dependency Tracking
Modern Makefiles should automatically track header dependencies:
DEPFLAGS = -MT $@ -MMD -MP -MF $(OBJ_PATH)/$*.d
-include $(DEPS)
3. Pattern Rules
Use pattern rules for scalability:
$(BUILD_DIR)/%.o: $(SRC_DIR)/%.c
@$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(DEPFLAGS) -c $< -o $@
4. Phony Targets
Always declare non-file targets as phony:
.PHONY: all clean flash help info
5. User-Friendly Output
- Use
@echofor status messages - Provide help and info targets
- Show memory usage after compilation
6. Safety Considerations
- Include confirmation prompts for dangerous operations.
- Use error checking where appropriate.
- Provide clear error messages.
Conclusion
Understanding Makefiles is crucial for embedded development, especially when working outside of IDEs or when you need fine-grained control over the build process. The examples provided show how to create maintainable, scalable Makefiles that can handle complex embedded projects. Key takeaways:
- Start with IDE-generated Makefiles to understand the basics.
- Use modern Makefile features like automatic dependency tracking.
- Organize your Makefile with clear sections and consistent naming.
- Always include user-friendly features like help targets and status messages.
- Test your Makefiles thoroughly and include safety features for dangerous operations.
Whether you’re working with AVR microcontrollers, STM32 devices, or other embedded platforms, these patterns and practices will help you create robust build systems that grow with your projects.